- Home
- Markets
- Cap & Trade
- Clean Fuels Standard
- Sustainable Fuels
- Carbon Offsets
- Carbon Linked Mechanisms
- Get to Know
- Market Coverage
- Cap & Trade
- Clean Fuels Standard
- Sustainable Fuels
- Carbon Offsets
- Carbon Linked Mechanisms
- Use Cases
- About us
- Membership Plans
- InSights
- Webinars
- Analytics Toolkit
- CAFÉ
- CAFÉ – Carbon Analysis Forecasting Engine Enter my CAFÉ
- Cap-and-Trade
- Clean Fuel Standards
- Carbon Offsets
- Articles
- Texas renewable growth spurs US voluntary RECs market
Texas renewable growth spurs US voluntary RECs marketNA RECsThursday, 15th June 2023
Nishant Kumar Upadhyay
Key highlights
- Renewable generation tracked by Renewable Energy Credit (REC) Program of Texas has been increased by 18% YOY in 2022.
- Low Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) requirement in Texas has led to a greater percentage of voluntary retirement of RECs in the state which has been 74% of the total RECs generation in 2022.
- The RPS mandate and REC requirement in Texas has increased by 12% since 2014, which resembles very less growth in RPS.
- Wind energy contributes more than 80% in total RECs generation in Texas.
Texas’ energy success story is not just a result of its abundant natural resources but also of its pro-business policies and free markets. The state’s energy sector is less regulated, which has created a favorable environment for competition and innovation, spurring the growth of renewable energy industry in Texas. The tax incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act, along with its tax credits is expected to accelerate this transition. It is still to be seen if Texas is capable to deal with the sudden growth of renewables. While Texas has benefited from the rise of renewables, the state’s low Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) requirements have led to REC generation being skewed towards the voluntary side. Texas is now leading the nation as the major source of voluntary retired RECs across the United States of America. In this article, we will investigate the increase in renewables generation, the number of RECs used for compliance in Texas and the number of Voluntary REC retirement by industries and utilities.
Renewable generation tracked by the REC Program of Texas has been increased by 18% YoY in 2022, resulting in a total of 138 million RECs generation

Figure 1: Renewable generation in Texas tracked by the REC program (Source: EIA and ERCOT Renewable generation in Texas) Note. The REC generation tracked is very close to the actual renewable electricity generated on the ERCOT grid reported by EIA.
Texas has significantly expanded its renewable energy generation, as seen by the Texas REC program. In 2002, only 2.79 million RECs were generated. However, with the issuance of various renewable promotion bills in 2007, the generation of RECs has experienced a remarkable surge. This growth can be observed in three distinct phases: The first after 2007 (41% increased of REC generation), the second after 2015 (23% increased of REC generation), and the most recent one after 2019 (18% increased of REC generation). As of 2022, the cumulative generation of RECs has reached an impressive 138 million RECs, which is 18% higher than 2021 generation and nearly 50 times higher than 2002.
Wind generation leads Texas renewable generation
Wind energy accounts for ~80% of Texas’ total renewable energy capacity, followed by solar, biomass, and hydro. Hydro energy capacity has been declining in Texas over the past five years. According to a recent study by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), drought-like conditions are threatening hydro power generation across many US states, and Texas is particularly affected by drought since 2014. While solar energy has historically lagged in the state, a remarkable surge of new solar capacity has recently been integrated into the grid. A total solar capacity of 14,762 MW has come online, resulting in the generation of 24 million Solar RECs in 2022.
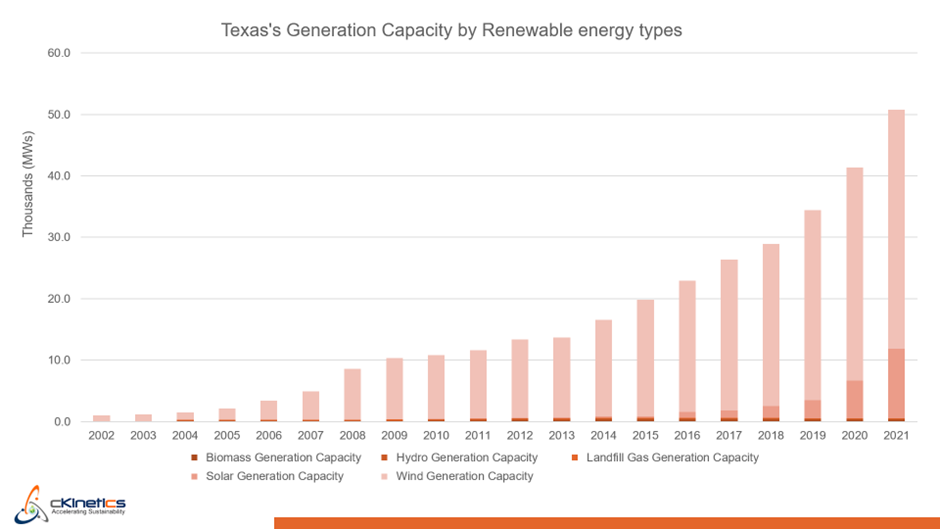
Figure 2: Growth of renewable generation capacity in Texas – by technology (Source: ERCOT report Texas)
RECs requirement for mandate only requires 15% of the total RECs generated in 2021
Renewable Energy Credit (REC) requirement of electric utilities to meet the RPS in Texas has seen a 12% increase since 2014. During the same period, the growth of renewable generation has experienced a significant rise of 64%. The number of RECs used for compliance has been shown in Figure 3. In 2021, only 17.15 million RECs were needed by covered entities to meet their compliance obligations. Since 2014, the RPS requirement for RECs has fluctuated between 15 million MWh and 17 million MWh.

Figure 3: RPS REC requirement (Source: ERCOT report Texas)
In addition to compliance RECs requirement, voluntary retirement along with previous years’ vintage voluntary retirement has increased in Texas.
Since 2016, the Power utilities’ retirement of voluntary RECs has continuously surpassed the retirement number of compliance REC. In 2021, power utilities retired 39 million MWh of voluntary RECs, while only 17 million RECs were mandated to retired for compliance purposes.

Figure 4: Total REC generation and retirement of Texas (Source: ERCOT report Texas)
In figure 4, RECs retirement does not match the RECs generated because RECs have a 3-year expiry and can be stored without retirement. Here, we can see the lag for some years where total retirement and generation has more gaps, which implies the retirement of previous years generated RECs in upcoming years. In 2022 the total generation and retirement are almost coverup the previous vintage REC.
Voluntary REC retirements reached over 100 million in 2022
Out of the RECs generated in Texas, very less share is either used for meeting compliance obligation of utilities or reaches expiry, the majority of available goes for the voluntary REC market. In the figure 5 below, we have mapped the growth of the RECs retired on a voluntary basis (green), along with the mandatory compliance requirements (red) and expired RECs (grey).
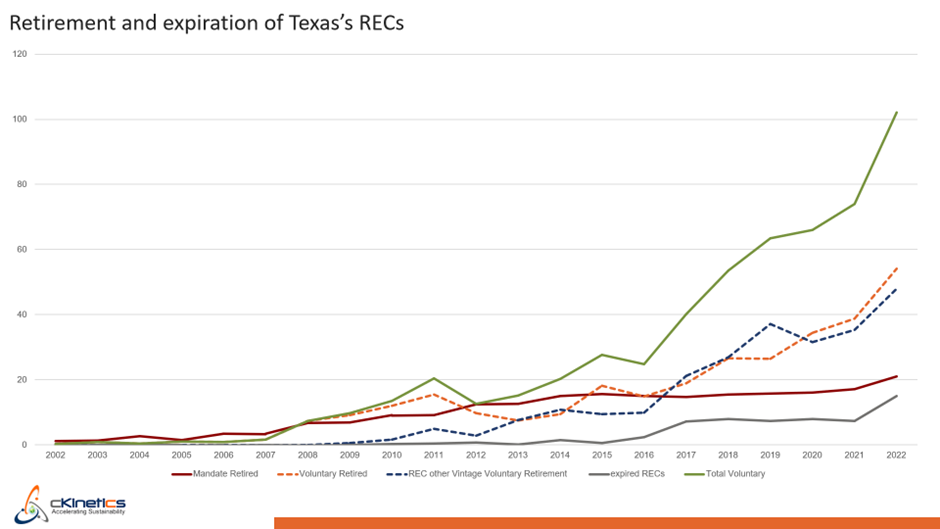
Figure.5: Status of Texas’s RECs retirement and expiration (Source: ERCOT report Texas)
Voluntary retirement of RECs by power utilities, corporates, and industries has been growing rapidly since 2015. As of 2022, voluntary retirement of Texas RECs now stands at 104 million RECs in 2022, nearly 75% of the total RECs generated in Texas. Out of which 56 million RECs were retired in the same year, and 48 million RECs were retired from previous years vintage REC. As the Texas renewable growth continues, we expect more voluntary RECs to be generated, which may result in a significant share exported to corporate organizations across the US. To sum that up, Texas has the lowest RPS requirement among the US states. This has led to a stagnation in the retirement of compliance RECs within Texas. Owing to this, the growth of renewable energy generation in Texas has largely translated into the growth of voluntary REC market. The presence of a 3-year lifespan for RECs in Texas has facilitated the retirement of previous vintages. As a result, Texas has solidified its position as the primary source of voluntarily retired RECs nationwide.
Table of Content
- Key highlights
- Renewable generation tracked by the REC Program of Texas has been increased by 18% YoY in 2022, resulting in a total of 138 million RECs generation
- Wind generation leads Texas renewable generation
- RECs requirement for mandate only requires 15% of the total RECs generated in 2021
- In addition to compliance RECs requirement, voluntary retirement along with previous years’ vintage voluntary retirement has increased in Texas.
- Voluntary REC retirements reached over 100 million in 2022
You might also likeArticles
Interviews
News
- No data Found!
Free Trial or Login to access
Our market portals and InSights are only for logged-in users with the relevant access. This can be you too…
Your Current Membership Does not Include this Content
This content is outside of your current package. If you need this too, let’s talk…
Solve Your Problems
Send this problem to our Clients team, and we will get back to you shortly with a plan of attack.
orSpeak and exchange notes with our specific-market expert, use your complimentary hours.
Arrange with Client TeamLet's Connect
Tell us who you are, and what you're after. We'll find you the right person with the answer - before you wake up twice.
Request Access to Data Tool
Tell us who you are, and what you're after. We'll find you the right person with the answer - before you wake up twice.
Newsletter Sign Up
Your name and email in exchange for staying up to date across the world's environmental markets... what a deal?!
MEMBERSHIPS
Sign Up for Free Trial or Login to Access Market Dashboard
Your Current Membership Does not Include this Content
This content is outside of your current package.
If you need this too, let's talk…My Saved Selections
Phasellus tempor tincidunt sem, sed dictum ipsum mollis vitae. Maecenas eu diam convallis, pellentesque lacus et, mollis enim.
ID # Custom Name Created On Insert From My Saved Selections
Phasellus tempor tincidunt sem, sed dictum ipsum mollis vitae. Maecenas eu diam convallis, pellentesque lacus et, mollis enim.
# ID Custom Name Created On My pinned contentThere is no pinned content to display - Clean Fuel Standards
- Clean Fuels Standard
- Cap & Trade
- Clean Fuels Standard
- Cap & Trade

